Do investors score with football stocks?
As anticipation builds for the new football season, we delve into the risk and return dynamics of football club stocks.
Summary
- Football club stocks are a rare example of both low beta and high volatility
- Their poor long-term performance is similar to risky stocks and unlike defensive stocks
- Football stocks are like lottery tickets and best left to speculators or die-hard fans
Although the majority of football clubs are privately held, enough are publicly listed to warrant in-depth exploration. These stocks might not be on every investor's radar, largely due to their low market capitalizations. This means their financial and economic impact is limited, which prevents their inclusion in mainstream stock indices.
However, their unique nature makes for an intriguing case study. For example, in October 2004, the stock price of Arsenal's "Invincibles" spiked by an impressive 67% after the team achieved an unbeaten streak of 49 games. Conversely, Juventus experienced a 45% drop in May 2006 following the revelation of the "Calciopoli scandal".1
Generally, a club's revenue is heavily tied to their on-field performance, where the line between success and failure is often razor-thin. Unlike conventional firms, football clubs tend to focus less on maximizing shareholder dividends, instead opting to reinvest earnings into their teams to enhance their potential for winning future matches and titles.
Our aim was to identify the most significant football stocks in terms of market capitalization, not only today, but also historically to avoid survivorship bias.2 Our sample consists of 26 football stocks from across a dozen European countries, typically competing in their respective local premier leagues. This includes well-known clubs such as Manchester United, Arsenal, Borussia Dortmund, Juventus, Olympique Lyon, and Ajax. A comprehensive overview of the included football stocks is given below in Figure 1.
Figure 1: Sample of listed European football clubs

Source: Robeco, STOXX. The figure visualizes our sample of listed European football clubs: Aalborg, AFC Ajax, Aarhus, AIK Fotboll, Arsenal, AS Roma, Benfica, Besiktas, Borussia Dortmund, Brondby IF, Celtic, FC Porto, Fenerbahçe S.K., FK Teteks, Galatasaray, Juventus, Kopenhagen FC, Lazio Roma, Manchester United, Newcastle United, Olympique Lyon, Ruch Chorzow, Silkeborg IF, Sporting Lisbon, Tottenham Hotspur, Trabzonspor.
Our sample spans from January 1997 to March 2023, offering over a quarter-century's worth of data. We gathered return and market cap data for each individual stock and constructed a football index by determining the capitalization-weighted average return of the available stocks at each point in time.
Initially, our football stock count is a mere 6, but the index gradually diversifies. Until 2005, the index is significantly influenced by Manchester United, with an average weight exceeding 40%. After Manchester United's delisting in 2005, the index becomes more balanced, a trend that persists even after Manchester United is relisted in 2012.
Low risk or high risk?
Our first analysis focuses on the risk associated with football stocks. The two most important risk measures are volatility and beta. For most stocks, these risk measures align closely, i.e., low-volatility stocks also tend to be low-beta stocks, and high-volatility stocks also tend to be high-beta stocks.
This relationship is illustrated in Figure 2, which classifies all MSCI Europe index constituents into three volatility buckets and three beta buckets independently.3 The graph demonstrates that most stocks fall along the diagonal from front left to rear right (blue bars), while stark differences between volatility and beta (red bars) tend to be quite rare.
Figure 2: Distribution of MSCI Europe constituents in volatility and beta groups
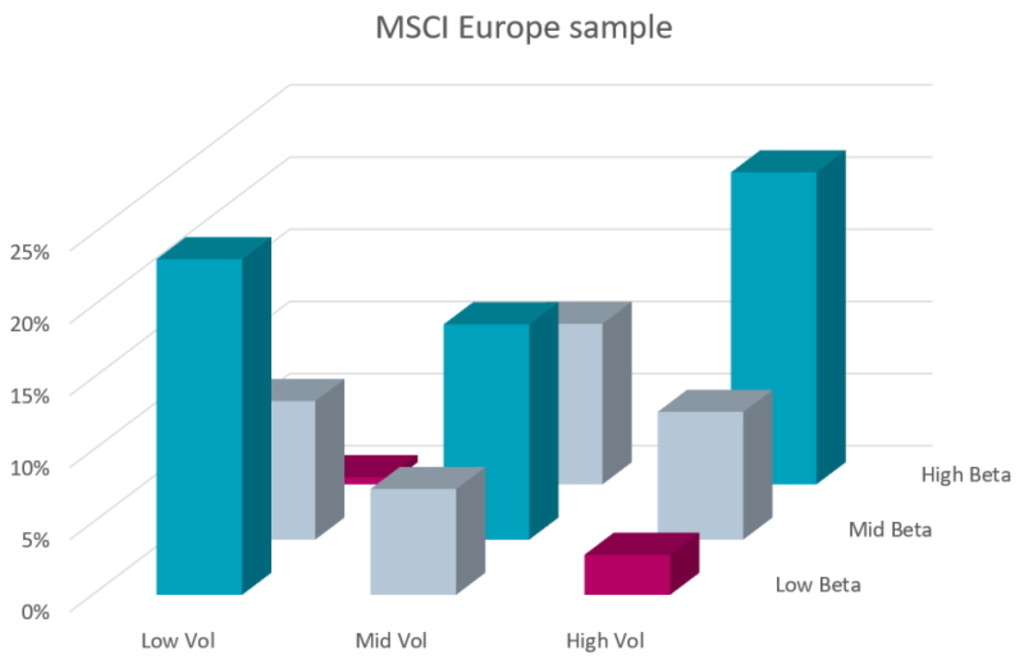
Source: Robeco, Refinitiv. The figure shows the distribution of MSCI Europe Index constituents in volatility and beta groups. To be included in the sample, we require at least five years of available return data. The sample period is January 1997 to March 2023.
However, football stocks exhibit very different risk characteristics. As shown in Figure 3, most football stocks simultaneously display a high volatility and a low beta, a very unusual combination. The high volatility means that share prices fluctuate widely, but the low beta indicates minimal co-movement with the market. In simple terms, the prices of football stocks go all over the place, but in their own unique way. Depending on the definition of risk, this makes them both low-risk and high-risk stocks at the same time.
Figure 3: Distribution of European football stocks in volatility and beta groups
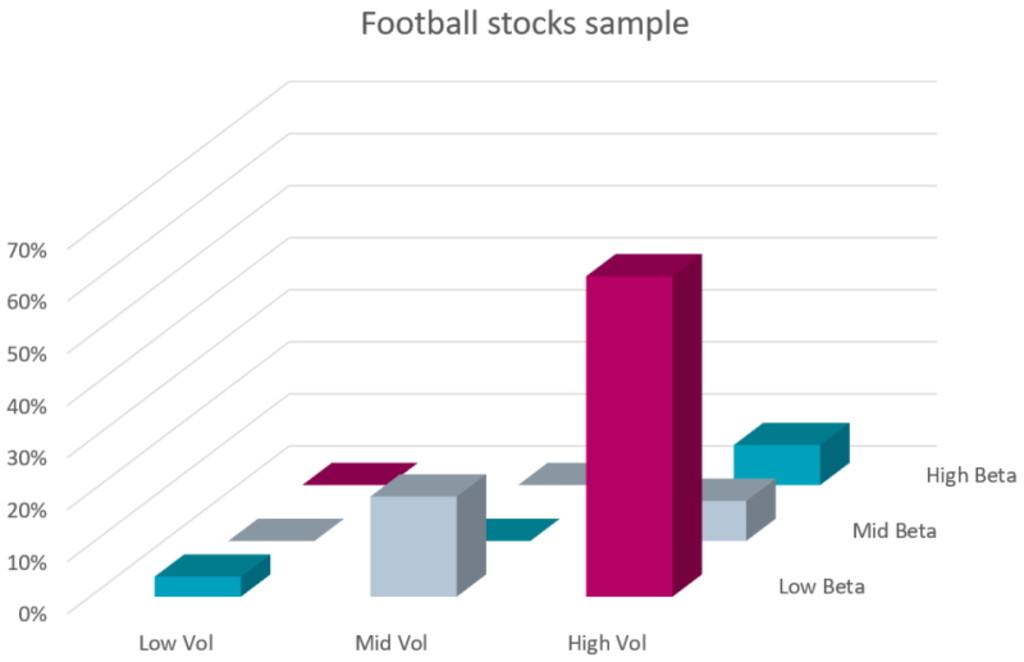
Source: Robeco, Refinitiv. The figure shows the distribution of Europe football stocks in volatility and beta groups. The football stocks are sorted into three volatility buckets and three beta buckets based on the same breakpoints as in Figure 2. The sample period is January 1997 to March 2023.
The return of football stocks
The return of the aggregate football index versus the MSCI Europe index by calendar year is shown in Figure 4. Return variations of 20% or 30% in a single year are no rarity, underlining the high volatility of football stocks. The low beta of football stocks is apparent in years like 2008 (global financial crisis) and 2022 (tech crash), when football stocks massively outperformed the market, demonstrating their rather uncorrelated behavior.
Unfortunately, large underperformances have been considerably more frequent (48% of the years) than large outperformances (just 30% of the years). Over the full sample, the return of the football index lagged the market by almost 6% per annum.
Figure 4: Calendar year return of football clubs versus MSCI Europe
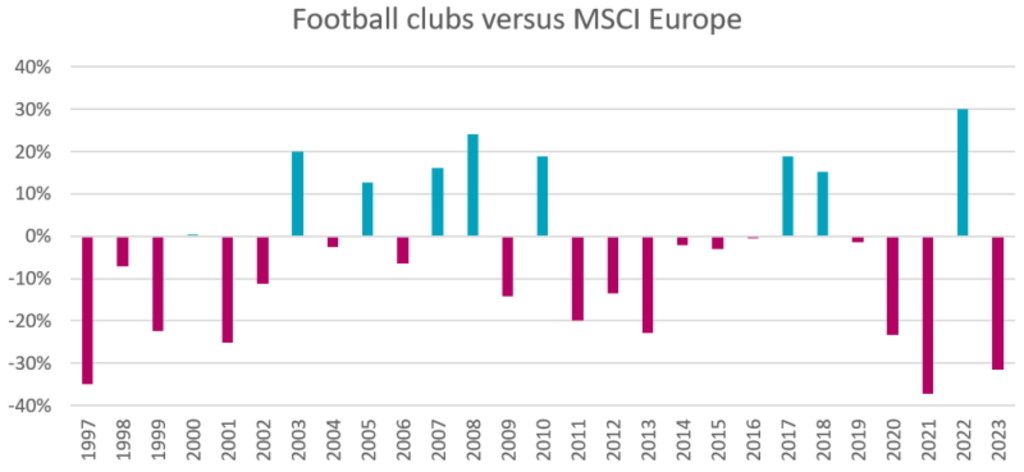
Source: Robeco, Refinitiv. The figure shows the return spread between European football stocks and the MSCI Europe Index. Portfolios are value-weighted and updated monthly. The constituents of the football portfolio are presented in Figure 1. The sample period is January 1997 to March 2023.
We have published extensively on the low-risk anomaly - the phenomenon that low-risk stocks deliver market-like (or superior) long-term returns with substantially lower risk, whereas high-risk stocks generate poor long-term returns despite their high risk.4 The same conclusion applies regardless of whether volatility or beta is used as a risk measure, which is unsurprising given their usual high correlation.5 However, football stocks, due to their contrasting volatility and beta characteristics, present a unique opportunity to assess which metric is a more important determinant of expected return.
To this end, we compare the long-term return of the football index with the returns of volatility- and beta-sorted portfolios in the MSCI Europe universe. We consider value-weighted tertile portfolios for volatility and beta estimated on daily data over a one-year lookback period. Figure 5 shows that the low-risk anomaly is clearly present among European stocks. In terms of long-term return, the low-volatility and low-beta portfolios come out on top, while the high-volatility and high-beta portfolios end up last. Although volatility seems slightly more potent than beta, the differences are small. This is consistent with the extensive literature on the low-risk anomaly.
Figure 5: Cumulative performance of football, volatility, and beta portfolios
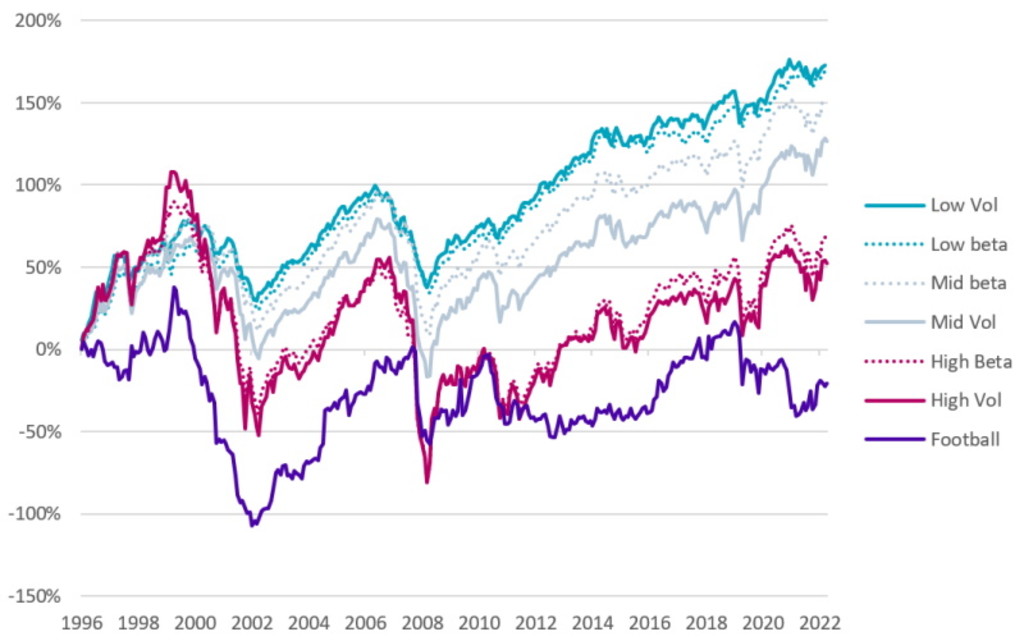
Source: Robeco, Refinitiv. The figure shows the cumulative excess return over the risk-free rate of European football stocks and stock tercile portfolios based on 260-day volatility and beta. Portfolios are value-weighted and updated monthly. The constituents of the football portfolio are presented in Figure 1. The investment universe of the tercile portfolios consists of the MSCI Europe Index constituents. The sample period is January 1997 to March 2023.
Turning to the portfolio of football stocks, we observe that they have the worst performance of all. In fact, their long-term cumulative excess return has been negative, meaning that an investment in football stocks underperformed even risk-free cash holdings. Given their extensive short-term return fluctuations and disappointing long-term average return, football stocks bear more resemblance to high-risk stocks than low-risk stocks. Thus, the high volatility of football stocks appears to be a better indicator of these stocks' performance behavior than their low beta. So when volatility and beta conflict, the evidence from football stocks suggests that investors should let volatility prevail over beta.
Get the latest insights
Subscribe to our newsletter for investment updates and expert analysis.
Football stocks as lottery tickets
A common rationale for the low-risk anomaly is that speculative investors willingly overpay for risky stocks due to a preference for lottery-like properties, i.e., a chance to hit the jackpot.6 Our sample contains some striking examples of this. For instance, Borussia Dortmund returned 138% in the 2010-2011 season when they unexpectedly clinched the championship after a long dry spell, Celtic returned 159% in the 2006-2007 season when they secured the national title and made it past the group stages in the Champions League, and Fenerbahçe generated a whopping 190% return in the 2007-2008 season when they reached the quarter-finals of the Champions League.
However, much like lotteries yield more losers than winners, the occasional big payoffs of some football stocks go hand-in-hand with poor returns in many other periods. Thus, while football stocks might be great for a lucky few who happen to choose the right club at the right moment, most investors end up disappointed.
Of course, die-hard fans might derive a certain non-financial utility from investing a small part of their wealth in the clubs they passionately support. However, from a purely financial perspective, the analysis in this article demonstrates that, despite their seemingly attractive low-beta characteristics, football stocks are generally not a desirable long-term investment opportunity.
Footnotes
1 Also known as the Serie A scandal. It erupted in May 2006 and implicated several top Italian football clubs, including Juventus, AC Milan, Fiorentina, Lazio, and Reggina, in a match-fixing controversy. Juventus was the most severely penalized, stripped of its 2005 and 2006 Serie A titles and relegated to Serie B with a significant points deduction for the 2006-2007 season. The scandal, which involved club officials influencing referee appointments, led to substantial changes in Italian football administration.
2 We looked at the constituents of football stock indices that used to be available in the past, which includes football stocks that have since been delisted.
3 Although our sample contains a few stocks from emerging markets (Turkey, Poland) or even frontier markets (North Macedonia) we use the regular MSCI Europe index as a reference point.
4 For an extensive overview we refer to Blitz, van Vliet, and Baltussen, 2020. “The Volatility Effected Revisited”, Journal of Portfolio Management, volume 64, issue 2, pages 45-63.
5 We tend to find slightly stronger results for volatiltiy than for beta but the main conclusion is the same.
6 See Barberis and Huang, 2008. “Stocks as Lotteries: The Implications of Probability Weighting for Security Prices”, American Economic Review, volume 98, issue 5, pages 2066-2100.
Important information
This information is for informational purposes only and should not be construed as an offer to sell or an invitation to buy any securities or products, nor as investment advice or recommendation. The contents of this document have not been reviewed by the Monetary Authority of Singapore (“MAS”). Robeco Singapore Private Limited holds a capital markets services license for fund management issued by the MAS and is subject to certain clientele restrictions under such license. An investment will involve a high degree of risk, and you should consider carefully whether an investment is suitable for you.