China in the Year of the Snake: Slithering over the bottom
In Chinese folklore, the snake symbolizes intelligence, mystery and renewal. So, will the Lunar Year of the Snake lead to the renewal of faith in Chinese equities and the economy, amid the mystery of how the country has slithered into deflation? Yes, says multi-asset investor Arnout van Rijn, who predicts a near-term bounce for stocks amid a bottoming macro outlook.
Summary
- Equities should outperform bonds if deflation can be conquered
- China is trying to move from an industrial to a consumer economy
- Trump tariffs are unhelpful but more depends on domestic confidence
Such has been the malaise of the Chinese economy – the second-largest in the world – that its domestic bonds have outperformed equities for the past four years, though the stock market has enjoyed a bounce due to excitement over artificial intelligence in the past six months.
Now it looks like the old snake is shedding its skin, though much depends on the end of deflation – where prices fall, undermining consumer demand that props up the economy – says Van Rijn, Portfolio Manager with Robeco Sustainable Multi-Asset Solutions. Deflation in Japan that began in the 1990s caused its economy to enter a near-permanent recession.
“We addressed the potential Japanification of China in our five-year Expected Returns, where we concluded then that China would not have to face the same ordeal as Japan went through due to much less leverage in property, better monetary policy, and no risk aversion among corporates,” Van Rijn says.
“The logical investment conclusion should then be that equity investors will outperform bond investors in the country. Chinese bond investors have benefited over the past four years, just like in Japan in the 1990s, from the move into deflation, just as Japanese equity investors benefited from the country moving out of deflation. Over the past six months, however, Chinese equity investors have been on the winning side. So, is this the end of Chinese deflation?”
“Chinese steel consumption is seven times that of the EU, while the EU and China are comparable in size by GDP. China is an asset-heavy economy in an adjustment phase: ‘build it and they will come’ has always been the approach. Successful for decades, it has recently run into trouble; the Chinese snake wants to shed its skin and move from investment-driven growth to consumption.
“This has been without success, as consumer confidence is low while income growth is falling back. Savings ratios are staying remarkably high at 44%. The two main reasons for the high savings ratio are a lack of (trust in) social security, which is secular, and weakness in property, which is cyclical, albeit a long drawn-out cycle.”
Tariffs versus growth
Efforts to revive the economy will not be helped by tariffs that US President Trump intends to impose on China to address the massive trade imbalance. The US trade deficit with the rest of the world widened to USD 78.2 billion in November 2024, of which USD 25.4 billion was with China1.
“The Chinese government will have to make some snake-like moves this year to reach its 5% growth target by improving domestic confidence, while at the same time dealing with a hissing US President,” Van Rijn says. “The fall in Chinese house prices has begun to level off, but we’ll have to see whether the Chinese snakes will be house hunting post-Lunar New Year.”
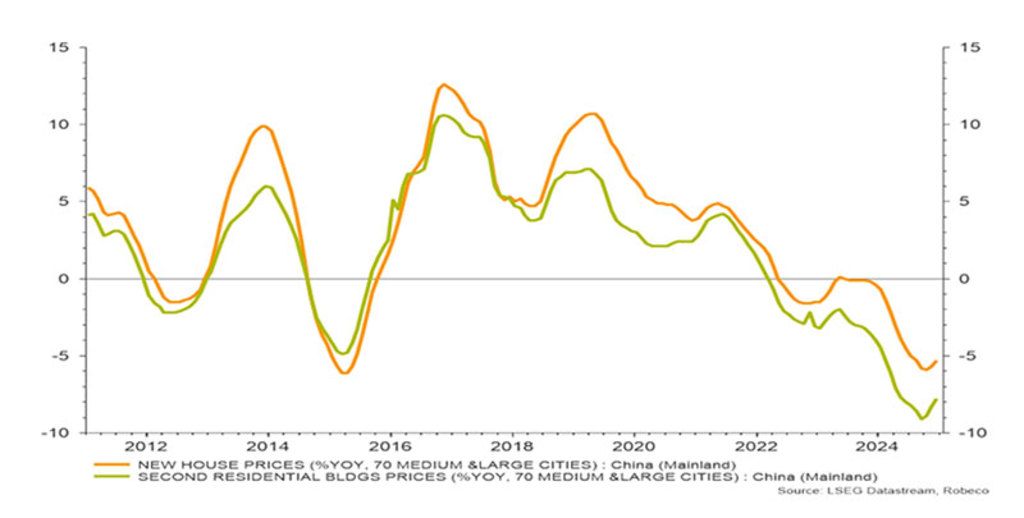
The fall in value in Chinese home prices, year on year. Source: NBS
“China has not seen serious inflation for over a decade as it kept money growth at bay. China saw inflation of just 2% in 2022 when the US and Europe were printing 8%. Deflation has now taken hold, just as debt positions are at a record high. That’s not good.”
“It is our view that this battle has not yet been won, and it will depend on future measures that may entice the consumer to spend. The National Party Congress in March is the next forum that may bring further clarity on this discussion. But don't bet on it... we expect the snake to slither along the bottom.”
Strength of the yuan
One focus for 2025 will be on the relative strength of the yuan. “For any emerging market investor, the quintessential question to ask is: ‘Do you believe the currency will be stable?’” Van Rijn says.
“Today, most people think the yuan is a weak currency, when actually, it is not. The international community focuses on the dollar cross rate far too much. Not much has changed versus the euro over the last decade.”
“Since 2021, the yuan has crept to stronger levels and is now within 5% of the 2015 painful strength level. Some depreciation may actually be in order, especially if the US starts another tariff attack.”
Get the latest insights
Subscribe to our newsletter for investment updates and expert analysis.
It’s now a broader stock market
So, what does this mean for Chinese stocks, which are often seen as a niche and volatile market? The news that Chinese firm DeepSeek had developed an AI model at a fraction of the cost of its US rivals injected a new energy into the mainland A-shares and the affiliated Hong Kong market.
“China is now a very broad and deep stock market,” Van Rijn says. “When DeepSeek became a hot theme, brokers immediately issued a list of a dozen beneficiaries. This is testimony to the longer-term appeal of China. Also, China's market cap-to-GDP ratio at just 56% today (versus 230% for the US), which gives some indication of the value opportunity.”
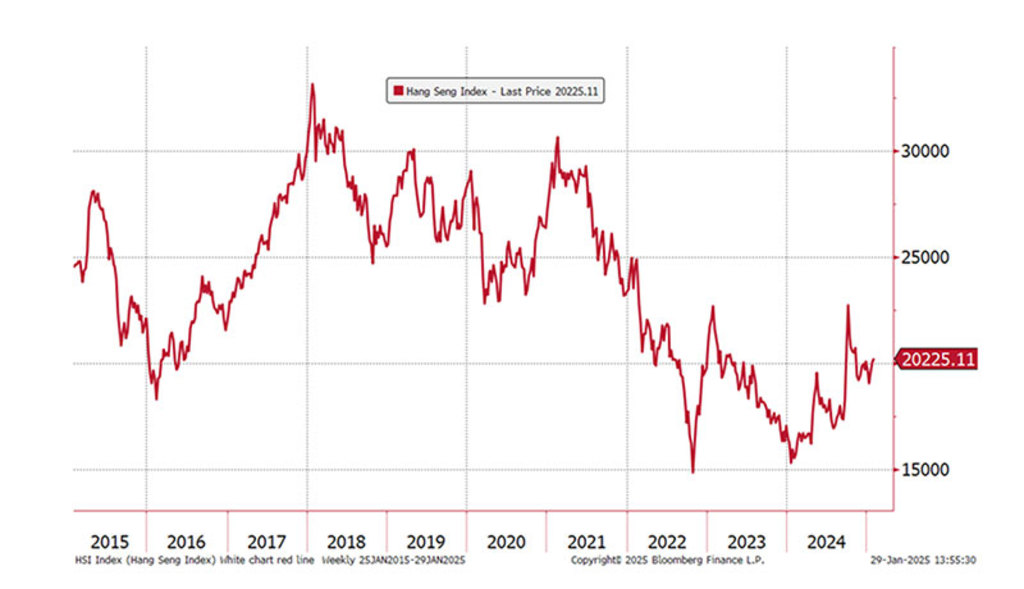
The Hang Seng Index has had a dismal decade, with a tentative bottom. Source: Bloomberg
US and Europe diverge on monetary policy
“Logically, with deflation not defeated, it is hard to be outrightly bullish. On the one hand, there is a risk of overcapacity and deflation, mostly for the industrials. Here, earnings revisions remain negative. On the other hand, we see strong policy support for equities, and many attractively valued large-cap companies that are not very dependent on the macro economy are showing positive revisions.”
“This explains our preference for offshore equities, where industrials are lightly weighted and the consumer and internet sectors are relatively heavily weighted. We see a Chinese equity bounce along the bottom, with tradable rallies in the Year of the Snake.”