
PFAS 2.0 – new waves of regulation will hit more than just chemicals
Regulatory ramp-up and class-action lawsuits open a new phase, new tools, and new investments in the fight against forever chemicals.
概要
- PFAS exposure linked to serious health issues
- The cost and scope of PFAS litigation and regulation expected to increase
- Testing, treatment, and destruction solutions poised for high growth
Over the past two decades, PFAS 1exposure from contaminated drinking water and soil has been linked with serious human health issues including birth defects and cancer. Tightening regulatory standards and costly class action litigation in recent years, is spurring investments in testing, treatment, and removal of PFAS from water supplies and the broader environment.
PFAS comprise a group of thousands of man-made chemicals. Small households to large industries are replete with PFAS-laced goods and processes – from non-stick pans and stain-resistant textiles to firefighting foams and chemical emulsifiers – earning them the title, ‘everywhere chemicals’. Their carbon-fluorine bonds are one of the strongest in chemistry, making them difficult to break down in the body and in nature. Their persistent nature has earned them another title, ‘forever chemicals’.
In 2023, major PFAS manufacturers agreed to settle up to USD 13.7 billion in class-action claims brought by hundreds of municipal water suppliers over PFAS pollution, with more suits still awaiting trial.2 To comply with new standards, clean-up cost estimates for water utilities for drinking water alone is estimated at around USD 50 billion over the next 20 years.3 President Biden’s Bipartisan Infrastructure Law of 2021 earmarks USD 10 billion in financing to help water utilities destroy PFAS and other harmful contaminants in water supplies.
Settlements and clean-up estimates thus far focus solely on water utilities. They exclude the cost of cleaning up PFAS seeping into soils and waste streams from landfills and contaminated industrial sites. In a 2021 report, the US Department of Defense estimated that USD 31 billion in federal funding was needed to help it clean up contamination on military sites.4
Clean-up cost estimates for water utilities for drinking water alone is estimated at around USD 50 billion over the next 20 years
Figure 1 – Suspected industrial discharge sites of PFAS (US, 2021)
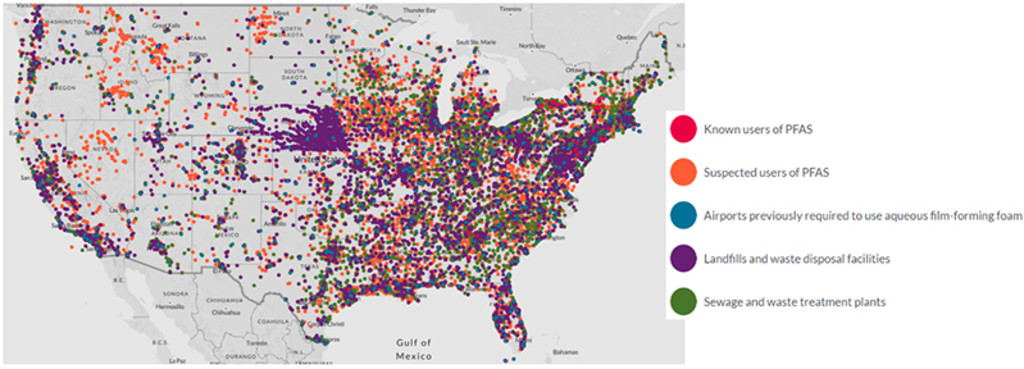
Source: The Environmental Working Group (ewg), 2021. The locations of 41,828 industrial and municipal sites known to produce, use or are suspected of using or sourcing PFAS. https://www.ewg.org/interactive-
An extensive problem
The problem is not limited to the military or chemical producers. From semiconductors to automotive manufacturing, many industries rely on PFAS inputs for their products. Regulatory action is driving many companies to launch alternatives with the same high-performance characteristics. But that may be tricky given the list of banned PFAS classes, chemical blends and concentrations may expand in the future. Moreover, companies are struggling to establish to what extent PFAS are used as inputs in manufacturing processes across product supply chains. Detection, remediation costs, (and lawsuits) will dramatically increase depending on how far regulators carry PFAS restrictions.
From semiconductors to automotive manufacturing, many industries rely on PFAS inputs for their products
Regulatory developments
In December 2023, the US Environmental Protection Agency (the EPA) published its second strategic roadmap with new standards for PFAS treatment and disposal in the environment. These will apply to companies producing PFAS or industries with PFAS-containing products. In early 2023, the EPA proposed new restrictions for six PFAS in public water systems.5 Once finalized, it should kickstart investments by water utilities at the federal level.
Europe is also combatting the problem. The EU set new limits for PFAS which will come into force among member states in 2026. Moreover, the European Chemicals Agency drafted a proposal to ban all ultra-toxic chemicals including over 10,000 PFAS compounds.
Figure 2 – Only at the tip of the triangle
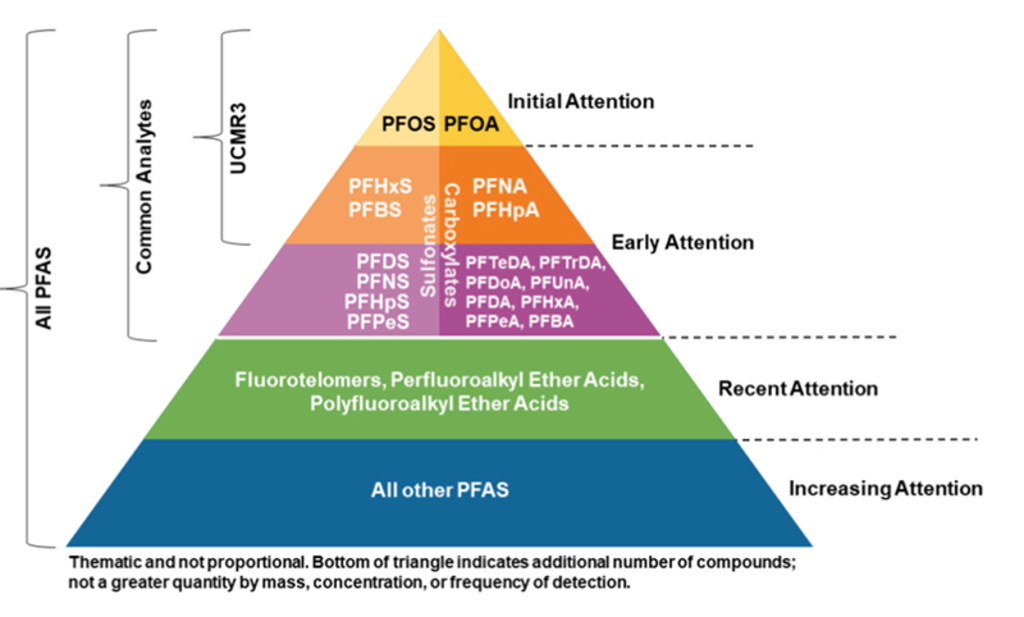
We’re only at the tip of the triangle. Regulation and litigation are expected to increase as attention on PFAS-related chemicals expands. Source: Regulatory guidance from the Interstate Technology Regulatory Council (ITRC). Per- and Polyfluoroalkyl Substances Team, September 2023.
Current PFAS management strategies
PFAS detection – Of the thousands of PFAS compounds that exist, commercial labs can generally test for the presence of only around 30 to 50 of them. Tests range from targeted analysis that can quantify the presence of specific, known PFAS compounds to non-targeted analysis which can detect whether a sample is PFAS-free. The latter allows for the much larger range of testing that will be needed to accommodate increases in regulated PFAS compounds as well as more restrictive concentration levels. Currently, the testing market size is small but expected to grow rapidly as regulations are passed to bring into scope not just water utilities but any company with tainted soil, air, or water.
PFAS separation – Conventional treatments to remove PFAS from contaminated water and soils include activated carbon filtration, anion exchange resin, nanofiltration, reverse osmosis, and foam fractionation. Many utilities have begun to invest in infrastructure upgrades that integrate more rigorous treatment depending on the scale and permissible contaminant levels. As with testing and measurement, expanding regulatory scope means upstream companies producing or using PFAS will most likely need to invest in PFAS treatment technologies to prevent discharge pollution in waterways and landfills.
PFAS destruction – Conventional treatment methods can remove PFAS from water and soils, but still leave behind dangerous concentrates. PFAS can be further treated and destroyed but methods used differ by cost, effectiveness, and scalability. A common approach is to incinerate or store PFAS-laden waste to prevent further leakage on land and in water. However, in addition to leaving pollutive byproducts, incineration is cost and energy intensive. For this reason, researchers are racing to find solutions that are sustainable in terms of cost, energy, and environmental waste.
A wellspring of growth opportunities
Fear of regulatory censure, fines, costly lawsuits, and reputational damage should push companies to ramp up detection and removal of PFAS byproducts within their supply chains. While current testing and treatment technologies offer a starting point, the escalating regulatory landscape and lawsuits will also drive demand for further innovation beyond conventional approaches.
The Sustainable Water Equities strategy invests in a diversified range of companies involved in the PFAS clean-up value chain. These range from the makers of instruments and analytics for testing to the technologies that enable its removal from drinking water, soils, and other solids. It also includes waste management companies responsible for PFAS destruction and storage as well as environmental service firms that help engineer cost-efficient remediation solutions.
The Sustainable Water Equities strategy invests in a diversified range of companies involved in the PFAS clean-up value chain
Moreover, the investment team is always on the look-out for promising technologies and new streams of growth. Though not yet commercially viable, electro-chemical oxidation, which breaks PFAS’s powerful molecular bonds and eliminates the need for costly incineration, may be the next big breakthrough.
In addition to Sustainable Water investments, Robeco is also using active ownership to keep waterways and the environment PFAS-free. The phase-out of hazardous chemicals is a targeted theme for Robeco’s 2024 multi-year engagement efforts with companies.
Footnotes
1Per-and polyfluoroalkyl substances
2Wall Street Journal, 26 December 2023. “Who pays to get forever chemicals out of drinking water.”
3Water Coalition Against PFAS Report, July 2023. “Correcting PFAS Myths: Misperceptions risk higher clean-up costs for water ratepayers.”
4
https://www.ewg.org/news-insights/news-release/2023/05/pentagons-contamination-time-bomb-cleanup-backlog-outpaces
5https://www.epa.gov/sdwa/and-polyfluoroalkyl-substances-pfas
獲取最新市場觀點
訂閱我們的電子報,時刻把握投資資訊和專家分析。
Important information
The contents of this document have not been reviewed by the Securities and Futures Commission ("SFC") in Hong Kong. If you are in any doubt about any of the contents of this document, you should obtain independent professional advice. This document has been distributed by Robeco Hong Kong Limited (‘Robeco’). Robeco is regulated by the SFC in Hong Kong. This document has been prepared on a confidential basis solely for the recipient and is for information purposes only. Any reproduction or distribution of this documentation, in whole or in part, or the disclosure of its contents, without the prior written consent of Robeco, is prohibited. By accepting this documentation, the recipient agrees to the foregoing This document is intended to provide the reader with information on Robeco’s specific capabilities, but does not constitute a recommendation to buy or sell certain securities or investment products. Investment decisions should only be based on the relevant prospectus and on thorough financial, fiscal and legal advice. Please refer to the relevant offering documents for details including the risk factors before making any investment decisions. The contents of this document are based upon sources of information believed to be reliable. This document is not intended for distribution to or use by any person or entity in any jurisdiction or country where such distribution or use would be contrary to local law or regulation. Investment Involves risks. Historical returns are provided for illustrative purposes only and do not necessarily reflect Robeco’s expectations for the future. The value of your investments may fluctuate. Past performance is no indication of current or future performance.





















