
SI Dilemma: Social or environmental – is the whole bigger than its parts?
At Robeco, we have always considered sustainability holistically. We started out integrating financially material sustainability issues in our investment processes. To also be able to analyze companies’ impact materiality, we developed a framework based on the 17 Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) and their underlying targets, thereby taking a holistic view on global sustainable development.
まとめ
- Environmental frameworks are progressing to include social objectives
- Products should state their contribution to social or environmental objectives
- Treating them as competing forces can create more confusion than clarity
Now the EU's Sustainable Finance Disclosure Regulation (SFDR) has swept into our lives and become mainstream since its initial publication in 2019. This EU regulation asks us to choose whether a company contributes to an environmental or to a social objective. We feel that this could lead confusion that becomes greater than the intended clarification. It gives rise to our SI dilemma: choose social or environmental?
Sustainability issues are ingrained into contours for mainstream investing today and it is clear that social and environmental matters are intertwined. This can be seen in the widely accepted framework that targets social and environmental issues under SDGs.
Frameworks that had previously solely focused on the environment have developed to also include social issues, and this appears not just as a climate transition, but in the development of the concept of a Just Transition.
The Earth Commission Global Commons Alliance, for example, has expanded on the important planetary boundaries concepts to construct a set of new Earth System Boundaries (ESBs). In addition to environmental limits, these ESBs include social metrics and social safety boundaries to minimize the harm caused by boundary breaches on human health and well-being, as well as addressing issues of fairness and justice.
Within the SFDR regulation, one of the many investment strategies requirements include setting up minimum commitments for sustainable investments that can contribute to environmental and/or social objectives.1 The European Commission advised that there must be no double counting of such sustainable investments, and where an investment contributes to both objectives, the investor must decide to which objective – environmental or social – the investment should be better aligned with.2
Robeco’s approach
Robeco operationalized such an ask through our own SDG framework, which we believe accurately assesses whether a company contributes positively to sustainable development and can therefore be categorized as a sustainable investment.
As is well known, the SDGs provide a holistic base including targets on a number of sustainability issues ranging from social issues (hunger, education, health care) and environmental concerns (biodiversity, climate change, marine, coastal, and water-related ecosystems). We can look through and segregate the 17 SDGs to identify social or environmental objectives.
For identifying companies that promote an environmental objective, SDG 12 (Responsible consumption and production), SDG 13 (Climate action), SDG 14 (Life below water) and SDG 15 (Life on land) we considered such factors relevant. Similarly, the SDGs identified as contributing towards social objectives were SDGs 1 to 11 and more specifically SDG 16 (Peace, justice and strong institutions).
These ‘social SDGs’ are mainly related to issues targeting improvements to society and community welfare such as the goals eradicating hunger, improving education, infrastructure and health care. Given the higher number of social objectives, it is likely that we would see a higher number of companies contributing to a social objective. Robeco internal data as of July 2023 depicts such results in the chart below.
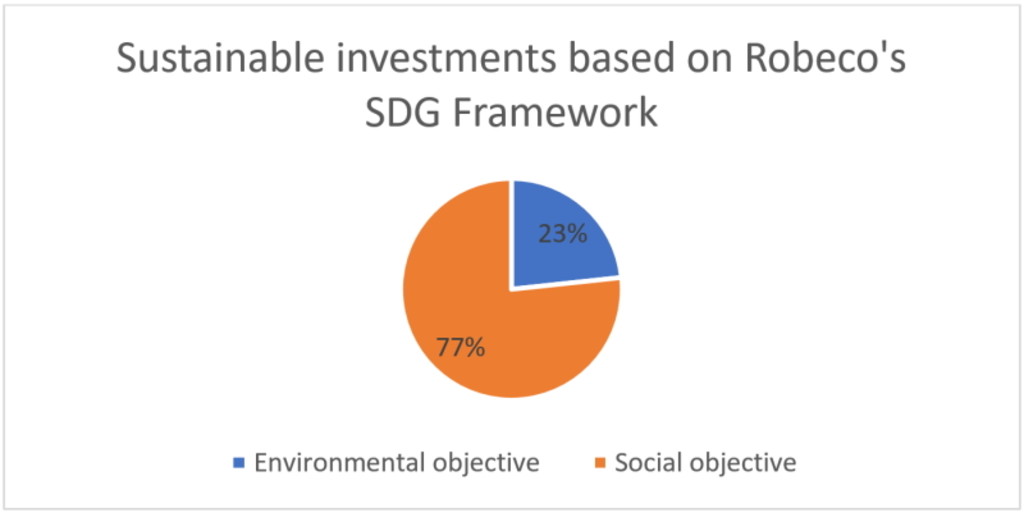
Data for SI as of July 2023 – Environmental or social3 in the corporate universe
Joined at the hip
While the above descriptors serve as a logical method to categorize companies across sectors and investment strategies, a closer look at the SDGs flags the complexities involved. It is commonly acknowledged that the 17 goals are interconnected, and actions taken to improve one objective do influence another SDG.4
Further, several SDGs have both environmental and social sub-targets. For example, SDG 7 (Affordable and clean energy) aims to provide access to energy for all (7.1 – a social goal), but also increase renewable energy generation and increase energy efficiency (7.2 and 7.3 – environmental goals). Similarly, SDG 6 (Clean water and sanitation) aims to improve human health (a social goal) as well as reduce water pollution (an environmental goal). Thus, at the heart of this conundrum, lies the question whether a clear choice on environmental or social objective can be made.
Invariably, such categorization also leads to assessment outcomes where companies could well be equally linked to both a social and environmental SDG. For instance, companies supplying insulation materials contribute to energy efficiency which is connected to an environmental goal (SDG 7) and a social goal (SDG 9: Industry, innovation and infrastructure).
Another example is companies that supply salmon to consumers and thereby provide healthy food contributing to SDG 2 (Zero hunger), which is a social objective. Under Robeco’s SDG Framework, such companies will only be positively scored on SDG 14 if they adopt environmentally friendly practices that can be verified with high certification levels (the ASC for fisheries and/or MSC for wild catches). If so, they can be classified as serving an environmental objective, even with a product that also serves a social intent.
We can find many other examples of companies for whom the social and environmental contributions they make through their products or services are intertwined. At Robeco, the criteria we use is to categorize them according to the highest impact that we think their products and services make, whether this be socially or environmentally.
SIディベート
Clarification or confusion?
But it’s not easy. Going beyond the company level and assessing commitments toward environmental or social goals from a top-down objective at the investment product level is formidable. It is no surprise then that an investment strategy can indicate an environmental objective through its portfolio names, but can also include many holdings which contribute to a social objective.
For example, a renewable energy investment strategy, which has a clear environmental goal, can show a higher commitment to making sustainable investments by using a social objective instead of stating its more obvious contribution to environmental objectives. We believe this creates more confusion than clarification.
Ultimately, for investors and clients, the precontractual commitments toward environmental or social goals should not be understood as representing the strategy’s overarching objective. These commitments are based in our view on the sustainability goal that a company aspires to, as explained above, and such views can differ. Investors should be aware of this dichotomy and therefore they need to keep a keen eye on what the strategy actually invests in.
We do understand that the European Commission does not want us to double count contributions, but at Robeco we view sustainability holistically, and believe in the dictum that there is no advancing the environmental goals without also having good social and governance practices. We feel that the whole is bigger than the sum of its parts. And who wants to argue with Aristotle?
Bhavya Sharma contributed to this column.
Footnotes
1 2022-12-02 | CSSF FAQ Sustainable Finance Disclosure Regulation (SFDR), p12.
2 2022-11-17 | Questions and answers (Q&A) on the SFDR Delegated Regulation, p32.
3 Qlik base in July 2023 data. Number of sustainable investments: 8411; Number of environmentally sustainable investments: 1954; Number of social sustainable investments: 6431
4 Pakkan, S., Sudhakar, C., Tripathi, S. et al. A correlation study of sustainable development goal (SDG) interactions. Qual Quant 57, 1937–1956 (2023).
重要事項
当資料は情報提供を目的として、Robeco Institutional Asset Management B.V.が作成した英文資料、もしくはその英文資料をロベコ・ジャパン株式会社が翻訳したものです。資料中の個別の金融商品の売買の勧誘や推奨等を目的とするものではありません。記載された情報は十分信頼できるものであると考えておりますが、その正確性、完全性を保証するものではありません。意見や見通しはあくまで作成日における弊社の判断に基づくものであり、今後予告なしに変更されることがあります。運用状況、市場動向、意見等は、過去の一時点あるいは過去の一定期間についてのものであり、過去の実績は将来の運用成果を保証または示唆するものではありません。また、記載された投資方針・戦略等は全ての投資家の皆様に適合するとは限りません。当資料は法律、税務、会計面での助言の提供を意図するものではありません。 ご契約に際しては、必要に応じ専門家にご相談の上、最終的なご判断はお客様ご自身でなさるようお願い致します。 運用を行う資産の評価額は、組入有価証券等の価格、金融市場の相場や金利等の変動、及び組入有価証券の発行体の財務状況による信用力等の影響を受けて変動します。また、外貨建資産に投資する場合は為替変動の影響も受けます。運用によって生じた損益は、全て投資家の皆様に帰属します。したがって投資元本や一定の運用成果が保証されているものではなく、投資元本を上回る損失を被ることがあります。弊社が行う金融商品取引業に係る手数料または報酬は、締結される契約の種類や契約資産額により異なるため、当資料において記載せず別途ご提示させて頂く場合があります。具体的な手数料または報酬の金額・計算方法につきましては弊社担当者へお問合せください。 当資料及び記載されている情報、商品に関する権利は弊社に帰属します。したがって、弊社の書面による同意なくしてその全部もしくは一部を複製またはその他の方法で配布することはご遠慮ください。 商号等: ロベコ・ジャパン株式会社 金融商品取引業者 関東財務局長(金商)第2780号 加入協会: 一般社団法人 日本投資顧問業協会






















